It is not every day that scientists come across a phenomenon so fundamental that it is observed across fruit flies, rodents and humans.
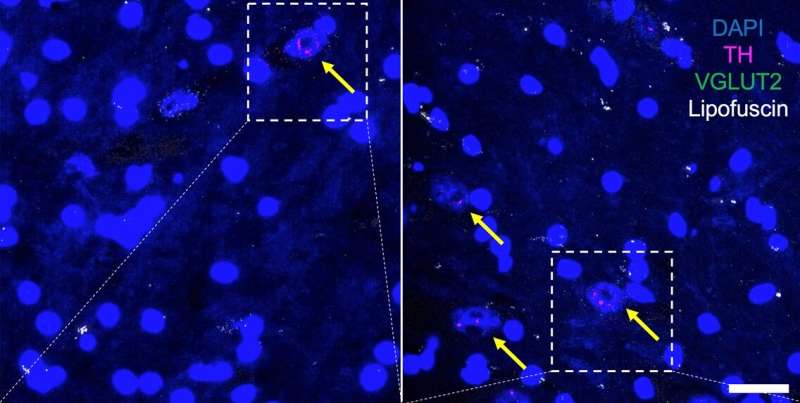
In a paper published today in Aging Cell, neuroscientists from the University of Pittsburgh Schools of the Health Sciences discovered that a single protein—a glutamate transporter on the membrane of vesicles that carry dopamine in neurons—is key to regulating sex differences in the brain’s vulnerability to age-related neuron loss.
The protein—named VGLUT—was more abundant in dopamine neurons of female fruit flies, rodents and human beings than in males, correlating with females’ greater resilience to age-related neuron loss and mobility deficiencies, the researchers found. Excitingly, genetically reducing VGLUT levels in female flies diminished their protection from neurodegeneration associated with aging, suggesting that VGLUT could be a new target for prolonging dopamine neuron resilience and delaying the onset of symptoms of aging in the brain.
“From flies to rodents to human beings, we found that VGLUT levels distinguish males from females during healthy aging,” said senior author Zachary Freyberg, M.D., Ph.D., assistant professor of psychiatry and cell biology at Pitt. “The fact that this marker of dopamine neuron survival is conserved across the animal kingdom suggests that we are looking at a fundamental piece of biology. Understanding how this mechanism works can help prolong dopamine neuron resilience and delay aging.”
Neurodegenerative disorders such as Parkinson’s disease are more likely to develop as we age. Parkinson’s disease—a slow but relentless loss of dopamine neurons in the brain that impairs one’s ability to move or talk—is known to predominantly affect men. But while biological sex differences, which arise from a combination of hormonal, genetic and environmental influences, seem to explain why females are protected from early stages of Parkinson’s, the driver and regulator of these protections was, until now, unknown.
Using a combination of biochemical and genetic techniques, as well as behavioral studies where flies’ locomotion was monitored for a 24-hour period, researchers found that age-related benefits afforded to females disappeared when the levels of VGLUT gene expression were significantly reduced in dopamine neurons.
“We found that VGLUT expression increases with age, and that flies become more vulnerable to dopamine neuron degeneration when we knock down VGLUT,” said lead author Silas Buck, a Ph.D. candidate at the Pitt Center for Neuroscience. “We also found that VGLUT expression is higher in females than males, suggesting that VGLUT may play a role in regulating sex differences in vulnerability to neurodegeneration in Parkinson’s and other neurological disorders where females are more resilient than males.”
As the rates of Parkinson’s disease are rapidly rising—the number of people affected by the illness worldwide is projected to reach 20 million by 2040—Pitt scientists hope to further probe the role of VGLUT in neuroprotection in humans.
Source: Read Full Article